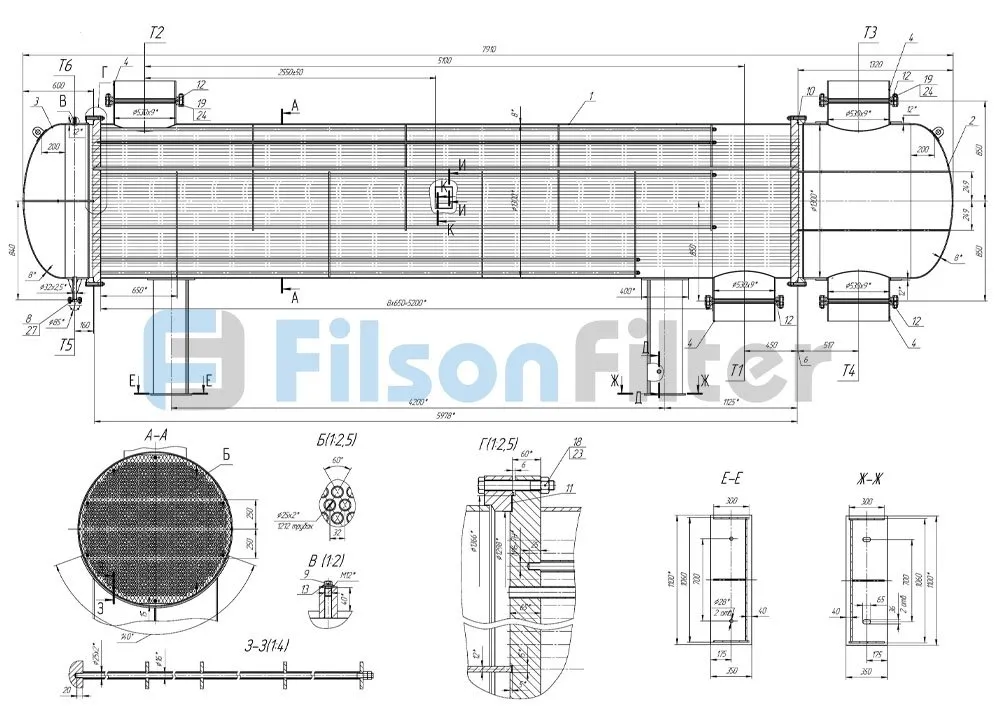
The Right Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger for the Application
Filson shell and tube heat exchanger is a device used to transfer energy from one working fluid to the other working fluid in the form of heat. During the process, the working fluid can be liquids or gases.
Filson shell and tube heat exchanger is currently the most widely used type of heat exchangers. It has a simple structure, reliable operation and various structural materials(mainly metal materials) manufacturing.
With over 20 years designing and manufacturing experience, Filson now is striving to provide the best shell and tube heat exchanger to customers around the world to help them run their industries or companies better.
Send us your fluids to be operated, desired temperature and pressure, shell and tube heat exchanger type or other specifications, Filson has experienced and well-trained engineering sales to come up with the most suitable solution for your application.
Filson Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
Why Choose Filson Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
- Reponsible Service and Support
Filson offers careful and considerate service for our customers. All our specialists are ready to support you from the initial shell and tube heat exchanger design stages to the installation and commissioning process, lasting for the entire lifetime of your heat exchanger.
- Guaranteed Quality and Performance
When buying a Filson shell and tube heat exchanger, you are not simply getting a heat-transfer device, you are investing in performance. Advanced technology and special equipments ensure the excellent quality and performance of your heat exchanger.
- Top-class engineering team
Filson possesses a veteran team of process, mechanical and thermal experts having sound knowledge in the field and seasoned employees who have worked for years. With them working together, a perfect shell and tube heat exchanger will be brought to you.
- Safe and quick delivery
Filson wins great reputation from multiple aspects including our delivery service. We promise to deliver immediately if there are shell and tube heat exchangers in stock and custom types within 20 working days. Also we will choose optimal transportation for you.

Filson: Your Reliable Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Supplier in China
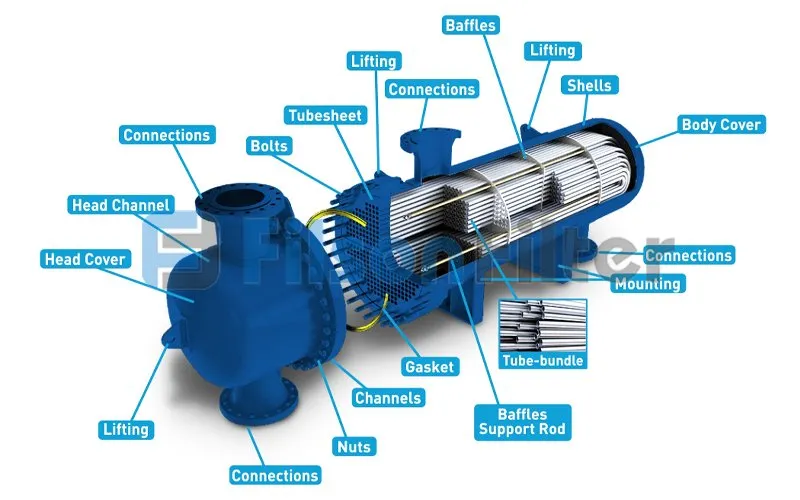
Filson shell and tube heat exchanger is essential for oil refining, power generation, chemical processing and more. And it has many shapes and sizes that can both introduce heat or remove heat.
Typically, a Filson shell and tube heat exchanger consists of two sections: one is shell side and the other is tube side or called channel side. In this type of heat exchanger, the tubes are always housed within the outer cylindrical shell.
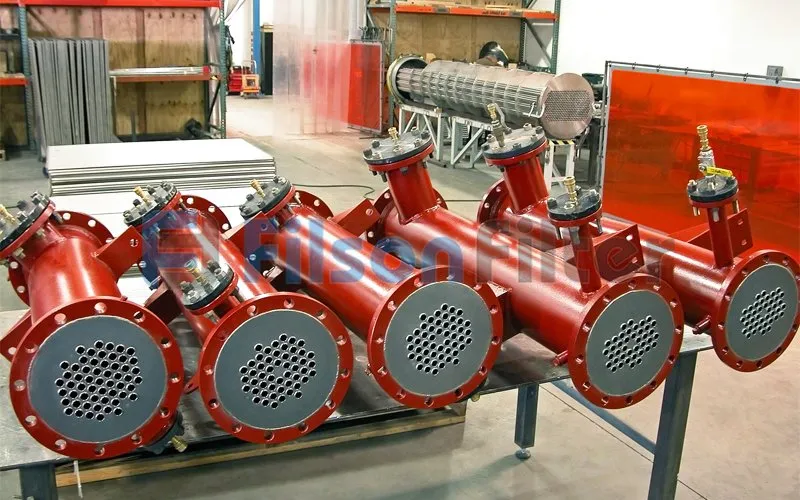

Filson builds shell and tube heat exchangers out of thermally conductive metals which transfer heat easily such as stainless steel, carbon steel, duplex stainless steel, aluminum alloys, etc. The tubes carry a fluid from the inlet to the outlet, while a separate fluid passes over these tubes in the shell.
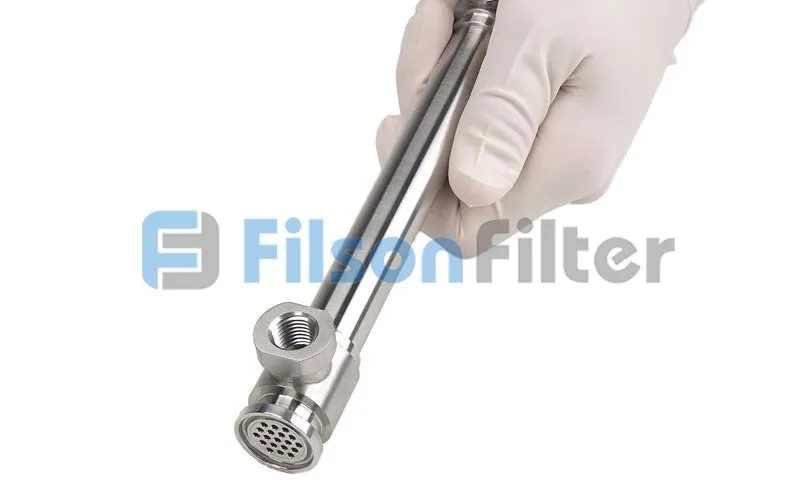
The number of tubes is also known as the tube bundle. It will decide how much surface area is exposed to the shell side, and therefore determine how much heat will be transferred. Filson, at this time, can introduce you a shell and tube heat exchanger design and calculations to meet your specific requirements.
In terms of shell and tube heat exchanger types, Filson has the ability to provide full kinds of them including but not limited to fixed tube sheet heat exchanger, floating head heat exchanger and U-tube shell and tube heat exchanger.
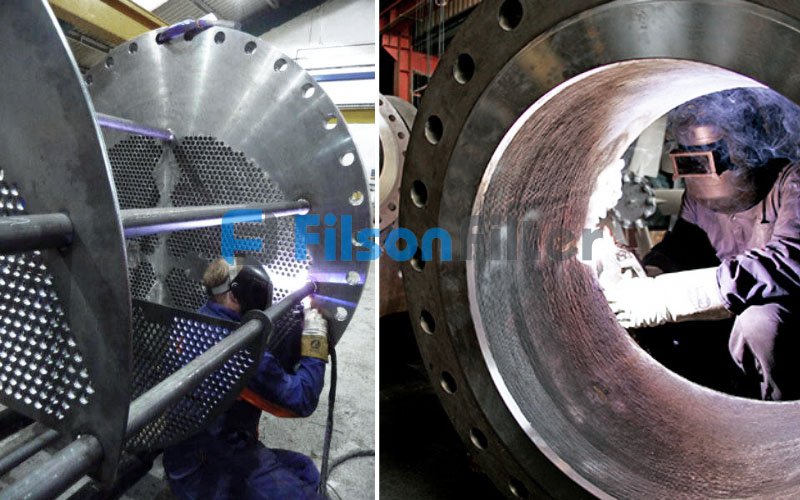

As one of the most professional shell and tube heat exchanger manufacturers in China, Filson will never let you down. Though to understanding what makes one heat exchanger unique from another is often difficult, Filson will accompany you to choose a suitable one.
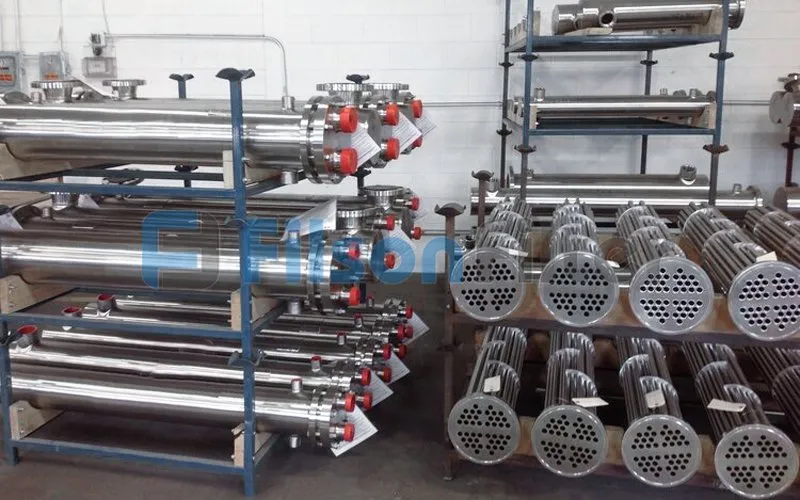

When choose or install a Filson shell and tube heat exchanger, you should take these factors into consideration: temperature difference between two fluids, the occurrence of phase change or not, type of fluids, pressure and temperature of fluids, etc.
If the temperature difference between two fluids is relatively small, you are recommended to choose a fixed tube heat exchanger. While a U-tube or floating head heat exchanger can be applied if the difference is large.
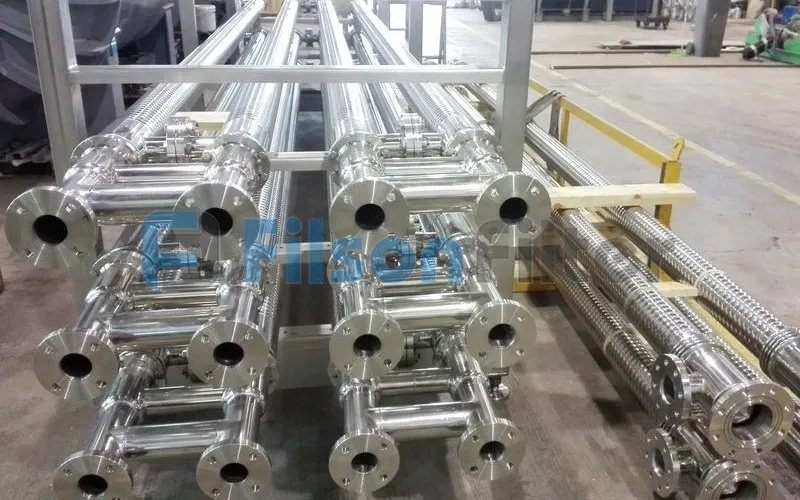

Filson shell and tube heat exchanger is ideal for demanding heat recovery duties under high pressure and temperature condition. Generally, this durable device can be made complying with ASME, JIS, GB or other standards.
Filson shell and tube heat exchanger is almost the most effective means of exchanging heat. The advantages of shell and tube heat exchanger can be summarized as high efficiency, compact structure, simple installationand mintenance and less energy costs.
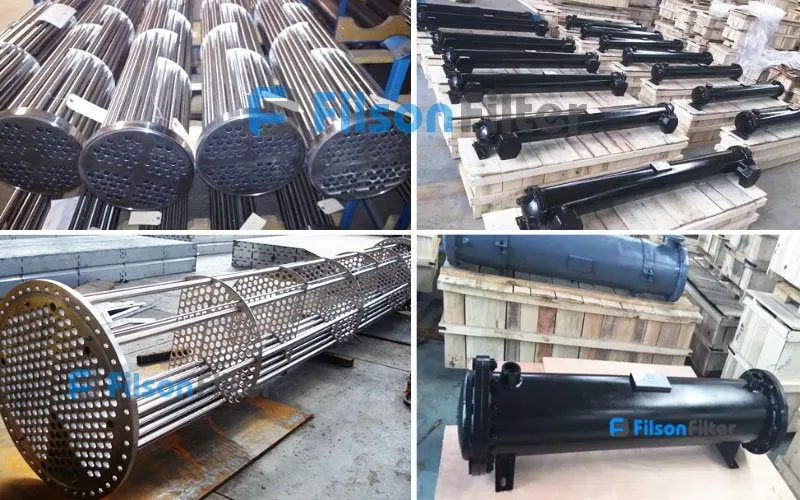

With such excellent performance and features, Filson shell and tube heat exchangers are widely distributed in many kinds of industries. If you are looking for a right heat exchanger for your manufacturing process, Filson will be your premier choice.
CONTACT US TODAY:
Phone: +86-157 3695 8886
Email: sales@filsonfilters.com
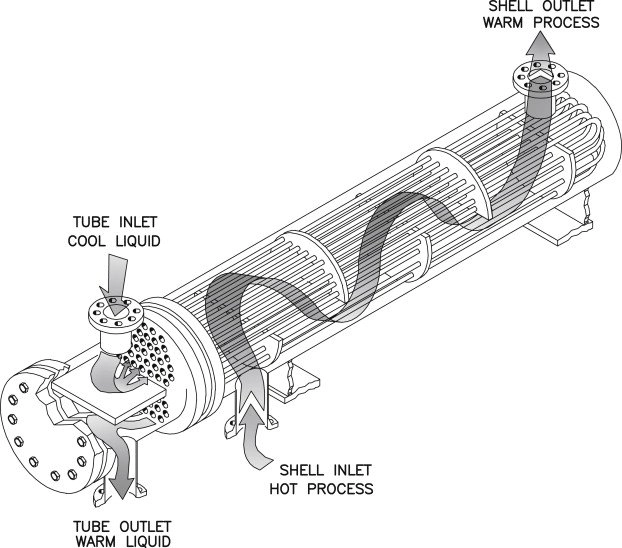
Working Principle of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger:
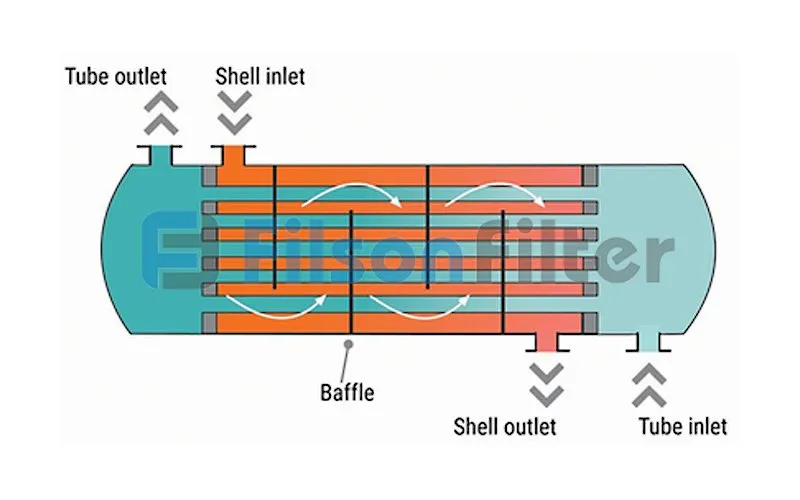
The work inside a shell and tube heat exchanger is fairly simple. There are two fluids, of different starting temperatures, flow through the heat exchanger.
One fluid flows through the tubes and the other flows outside the tubes but inside the shell. During this process, heat is transferred from one fluid to the other through the tube walls. The fluid inside the tubes is either heating or cooling by the other fluid outside the tubes.
The fluids on the shell or the tube side can be either liquids or gases. In order to transfer heat efficiently, a larger heat transfer area is required which can be realized by using many tubes. In this way, waste heat can be put into use wisely leading to efficient energy conservation.

As shown in the figure above, it’s the basic working process of Filson shell and tube heat exchanger.
Filson Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Function:
- Optimize energy efficiency
- Heat or cool a specific fluid
- Increase profitability and gain better ROI ( return on investment )
- Improve sustainability and lower environmental impact
- Benefit a large amount of industrial applications
- Replace existing equipment due to wear and tear
- Upgrade existing equipment to newer more efficient designs
Filson Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Feature:
- Outstanding thermal performance
- Superior hydraulic efficiency
- Efficient heat transferring
- Optimal solution for various applications
- Easy to dismantle, clean and repair
- Durable for a long term use
Filson Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Specification:
- Material: stainless steel, carbon steel, manganese steel, copper, aluminum, titanium
- Media type: oil, water, air, gas
- Structure: single channel, double channel and multi-channel
- Shape: fixed pipe plate, floating head, U-type pipe
- Working temperature: under 450℃(up on material and type)
- Working pressure: under 6.4MPa
- Flow rate: 25L/min(depending on fluid type)
- Heat transfer efficiency: 2.80% to almost 100%
- Heat exchange area: 1 – 800㎡
- Color: grey, blue, silver, brown(based on customer requirements)
- Standard: ASME, ANSI, JIS, GB
Filson Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Application:
- Refinery and petrochemical
- Fertilizer
- Preheating
- Oil and gas
- Chemical processing
- Power plants
- Steam generation
- Vapor recovery systems
- Industrial paint systems
- Combustion air heating or cooling
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers: The Ultimate FAQ Guide
Like a Heat Exchanger, Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers are equipment that helps facilitate the transfer of energy from a functioning fluid to the next whether as liquids, gases, or solids.
In essence, this device places two functioning fluids in thermal closeness via tubes encased in shell cylindrical in shape.
For efficient operation, this device must have a number of components.
Without these parts, the device may fail or perfume poorly.
Here are the parts of this equipment:
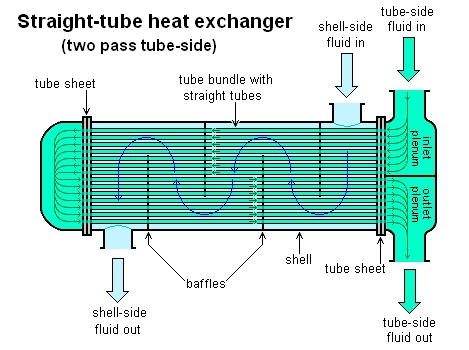
Shell and tube heat exchanger
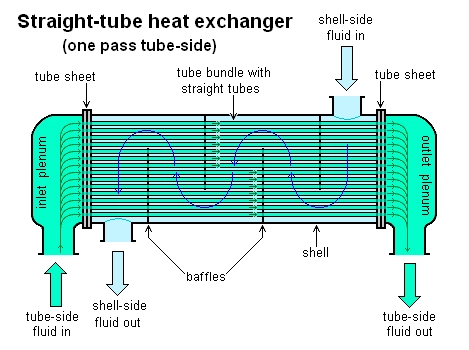
Shell and tube heat exchanger system
· Shell
This part is the first thing you notice when you come across a Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger.
Outer shell is characterized as the casing of this device housing all the parts of a Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger.
It also holds the process fluid.
· Ports
Ports are connections that avail hook ups for the process mediums.
The ports could be NPT type connections or face flanges.
Tube side fluid in
Tube side fluid out
Shell side fluid in
Shell side fluid out
· Enhanced Surface Tubes
There are several tubes encased in the device, and they come in a bundle.
Tubes transport the fluid from the entry to the exit via the fluid flow process on the tube-side.
Tube is often removable for service and maintenance purposes.
Tubes must be resilient to large temperature differentials/fluctuations, have excellent thermal transfer properties, and resistant to corrosion.
When selecting a Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger, tube material is a key consideration.
Some of the tube materials include brass, copper, and different steel alloys.
These materials are suitable for tubes because of their exposure to stress that occurs due to being subject to the temperature differential.
· Plain Tubes Single/Two-phase Heat Exchangers
An exchanger with a single-phase lets the phase of the fluid remain constant all through the whole process.
What happens is that a liquid enters the device leaves the device as a liquid.
An exchanger of two-phases typically causes a stage-change when the transfer of heat occurs.
What happens in this case is that heat enters the device and leaves as a liquid.
· Baffles
Baffles are barriers located within the shells.
Baffles optimize the general volume of thermal mixing that takes place in the coolant pipes and the fluids in the shell-side of the device.
They create turbulence within the encasing (shell) to reduce concentrations and improve the efficiency of cold or hot.
While baffles are simple design concentrations, they are key to proper function.
· Turbulator
A turbulator is an insert which forces a turbulent flow via the tubes and prevents fouling or sediment processing.
Turbulator also increases the capacity of the exchanger’s heat transfer.
· Outlet/Inlet Plenums
They are found on the end of the device.
It is the open area where the tube bundle discharges or collects the cooling fluid.
This device works on the idea that a hot fluid passing over/around a colder fluid transfers its energy in the cold flow direction.
A Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger has two inlets and outlets each positioned strategically on opposite sides.
Every fluid enters the device through the respective inlets and exists via a respective outlet.
The tube-flow goes through the tube bundle and exits through the tube outlet.
Tube-bundle is secured by tube plates or metal plates referred to as tube sheets.
Similarly, on the second part of the device (shell-side), fluid passes through the case’s inlet to the tubes and then leaves through the outlet of the device.
Further, the headers positioned on the two opposite sides of the tube bundle develops storage areas for the flow on the tube-side.
It is often divided into parts depending on the particular type of heat exchanger.
A turbulator positioned in the tubes causes a turbulent flow of fluids.
Also, baffles in the shell help maximize the volume of thermal mixing that occurs in between the shell-side fluid and coolant pipes.
The shell-side fluid moves via the baffles causing the fluid movement to repeatedly go past the tube bundle.
In the end, the fluid transfers energy and then exits the device at a lower temperature.
Fluids can pass through the device once or several times via a single-phase exchanger or two-phase exchanger respectively.
This machine is used in many industries and comfort applications for cooling and heating fluids.
They have several applications due to their compatibility with both gas and liquid.
The applications are:
- Condensers
- Coolers
- Process heaters
- Reboilers used for
There could be design subtleties for specialization in the application, however, this device contains some consistent features which are responsible for its design.
There is a pressure differential so that if there is an unexpected leak, the cross-contamination problem is limited.
Normally, the pressure would be greater in the tube shell, hence, if an unexpected leak occurs the process fluid flows into the cooling medium.
Such a design prevents the process fluid from being contaminated.
Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger has these additional features:
- Baffles
- Inlet/Outlet Plenums
- Four Ports
- Tubes/tube material
- Shell; it is the outer portion of the device holding the process fluid and housing the internals.
Even so, there are two main ways of design for this equipment.
They are mechanical and thermal design.
Thermal design is done using computer programs from Heat Transfer Research Incorporated and Heat transfer and Fluid Flow Service.
There is a focus on calculations such as pressure drops, heat transfer coefficients, sides fluids are allocated and tube size among others.
The mechanical design of the device provides information on issues such as flange thickness and shell thickness.
These aspects are calculated with the use of a pressure vessel code. However, ASME is the popular code for this machine.
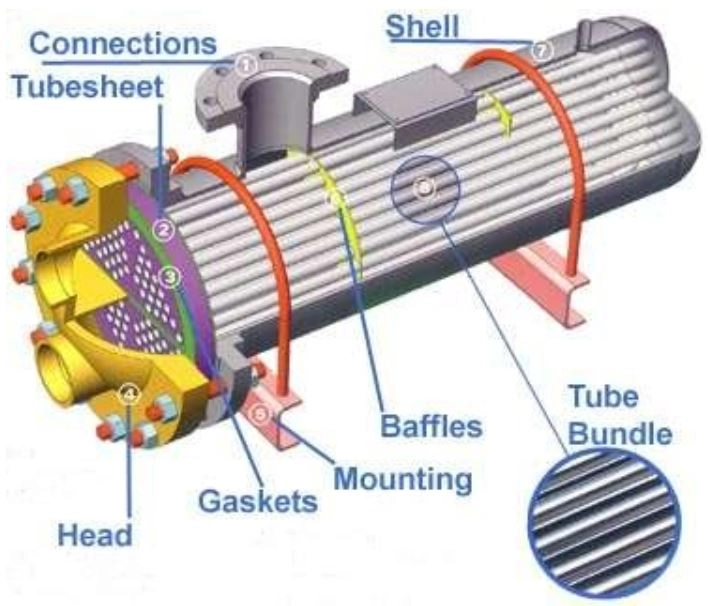
Shell and tube heat exchanger system
There are basic types of this equipment and their regulation is by (TEMA) Tubular Exchangers Manufacturers Association.
According to TEMA, there are three types of equipment that are built uniquely to serve special purposes.
The designs are focus on aspects such as the shell, the back header and the front-end header.
These parts are then labeled using letters for easy identification.
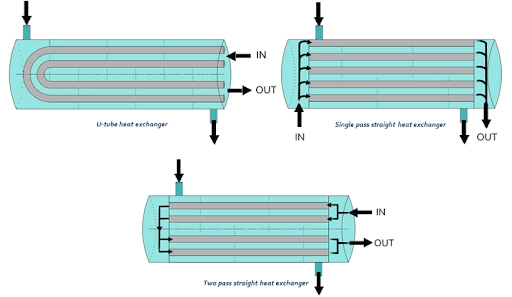
- U-Tube
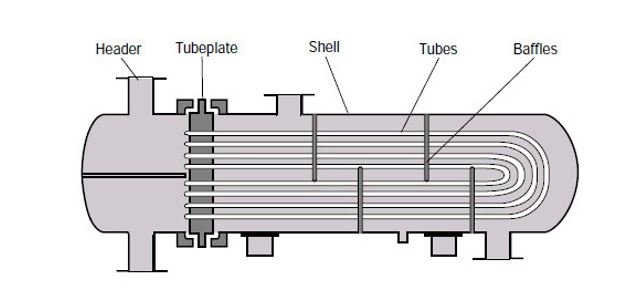
Shell and tube heat exchanger system
For this device, the main component, tube bundle, consists of several tubes that easily bend directly into a U-shape.
One tubeplate connects the tubes and the shell.
The cooling fluid option moves through the U-tubes from the upper half of the header and leaves via the lower half of the header. As such, it creates a multi-pass design.
It has a bend that enables increase in size due to heat to occur without applying expansion joints.
The reason for this is because bend-side of the equipment is free-floating in the shell and it lacks space for expansion/contraction.
It is imperative to understand that cleaning the bend sides of this device is difficult.
Nevertheless, it is suitable when using high-temperature differences in places expansion is anticipated.
· Fixed Tube Sheet
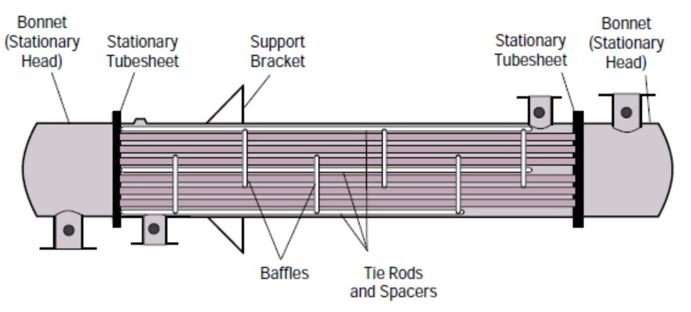
Shell and tube heat exchanger unit
This device applies two stationery tube sheets often welded on the shell.
Fixed tube sheet exchanger is easy to manufacture as well as the most cost-effective.
The expansion should be prevented in this device as tubes are tightly attached to the casing through the tube sheets.
Operators may suffer damage or expansion if the temperature difference is high.
That is, especially between the shell and tube-side flows, hence, temperature-difference has to be kept very small.
Besides, the outside of the tubes is not accessible for cleaning.
In the event that you foul the exterior of the tubes using the cooling fluid on the shell-side, the efficiency of the shell and tube heat exchanger will reduce.
· Floating Head Heat Exchangers.
This device combines the best of the other above two devices.
While one side of the device is free to expand using a floating tube sheet, the other end is attached still to the housing using a fixed tube sheet.
Due to the tube sheet, the tubes can increase in size with enhanced temperatures.
This process occurs simply and it does not disform the pipes.
Those operating this device creates a difference in high-temperature without being fearful of destroying the equipment.
It is also easy to clean the insides of the tube.
This type of Heat Exchanger is the best type for use in different processes.
Its only downside is the high cost; however, it has excellent maintenance and efficiency.
When considering purchasing a shell and tube heat exchanger, a Floating head heat exchanger is the most preferable choice.
From the most complex to the simplest chemical process systems, shell and tube heat exchangers are needed to undertake the basic and important functions.
That is, the functions of efficiently transferring heat from one medium to the next.
Regardless of which industrial sector you intend to use your device in, you are practically looking for the same equipment that will efficiently get the said job done.
Even so, below are the factors to look for when buying this type of heat exchanger:
- The Material you use for Building the Device
This factor shows whether the material chosen for the device puts it under extreme stress when exposed to high heat/temperatures.
Also, the material has to be able to stand any potential corrosion.
- Application
The device you choose, should be able to perform well to carry out your process objectives.
If using the device in pharmaceuticals, one has to make sure that it is structured in such a way that it can efficiently perform its role.
- Accessibility to Utilities
The shell and tube heat exchanger should have a connection to its application whether it is steam, cooking oil or water
- Cost
You have to consider how much the suitable shell and tube heat exchanger costs.
The overall cost caters to maintenance, purchase, operating, and installation costs.
- Scalability
The focus is on whether the device will manage to address the heat transfer needs of the current system and potential future process developments.
- Characteristics of Thermal Fluid
What thermal fluid does your shell and tube heat exchanger use will determine the type of device that you buy.
- Operating Specifications
The type of device chosen should be at par with the temperature and pressure ranges used during different phases of the process.
- Environment
The carbon footprint the device leaves is essential. Also, the device has to be energy efficient.
The reason why one would opt for this machine over other types of heat exchangers is because of some properties they possess.
Some of these properties include:
- Can withstand high temperatures and pressures. Its cylindrical design is very resistant to pressure allowing every range of pressure applications.
- Are versatile which is why they are popular and widely used in the process industry
- It has a long lifespan
- Flexible as they come in different sizes and orientations
- Easy to service and this is due to the floating tube bundle.
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers are made out of thermally conductive metals that enable easy heat transfer.
The materials also offer the device protection against corrosion effects.
Your choice of material should depend on the fluid you intend to use.
The materials used to make the Tube part of the device are:
- Stainless steel
- Copper
The materials used to make the shell side of the device are:
- Stainless steel
- Brass
- Copper
Some of the liquids used in Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers are:
- Steam
- Hydraulic Oil
- Deionized Water
- Machine Oil
- Salt Water or Motor Oil
No.
There are no size limitations to shell and tube heat transfer system.
You can access a device of a larger or smaller size.
The pipe size of the shell and tube are diverse ranging up to 3 inches and 6 inches.
The overall length can be up to 87 inches.
The surface areas can be up to 92.7 square feet.
The same goes for the diameter and height of the tool which goes for up to 15 inches. the
There are two types of connections for this device’s shell side:
- Threaded Connection
- Flanged Connection
The maximum pressure of the shell side of the Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger varies depending on the material used for its construction.
A Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger can have a maximum pressure of:
- 100 PSI
- 150 PSI
- 225 PSI
- 250 PSI
- 300 PSI
- 1,000 PSI
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers have to meet a set number of quality standards that guarantee the safety and quality of the products.
You have to ensure that your Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger is designed and built according to the right industry standards.
With the mark, the product can be traded in the various markets.
Some of these quality standards include:
ASME
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers with the ASME code meet ASME pressure vessel code for over-pressurization
- ASME standard boiler code
TEMA
- Tubular Exchanger Manufacturers Association aids in the definition of the manufacturing tolerances, as well as machining, applied when constructing this heat exchanger.
- A user understands that a device with a TEMA mark meets industry standards and built in a way to reflect quality.
The three main classes of rating are:
TEMA R – Refinery Service
TEMA C – General Service
TEMA B – Chemical Service
PED
Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) is an international standard often required in the European Union.
Different nations have varying rules about what standards a Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger has to meet to be legal.
This standard covers a wide scope of equipment ranging from pressurized storing vessels to piping and boilers.
Some of the rules that PED covers include:
- Essential requirements
- Materials
- Harmonized standards
- Conformity assessment
- Market surveillance
CRN
Canadian Registration Number is needed for any Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger that will be in use in Canada.
This number is often written with several digital numbers, a decimal, and several numbers/letters that represent a nation or province.
When you buy a Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger make sure that it has the right certification.
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers are sold at competitive prices.
The manufacture of this device requires specialization.
Cost covers installation, purchase, maintenance, and operating cost.
You have to fabricate the materials before building the final device.
In addition, you could paint the shell or inside walls of the device to offer further protection from corrosion or other effects.
A Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger can cost as high $8,000 and low as $600.
The prices vary depending on the material used to make it, surface area, pipe size, maximum and minimum temperatures/pressures, cooling/heating capacities or the number of passes.
The design temperatures of the shell side of the heat exchanger is -2500C to 8000C.
Shell and tube heat exchanger
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers are mainly used for cooling and heating systems.
They are often used in engine cooling systems and in refrigeration.
Also, they are used in refining oil, the brewery of alcohol, preparing pharmaceutical products, and producing quality and safe food products.
While a Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger with ASME code mark are costly, it is of high quality.
Some of the reasons why people go for Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers over other Heat Exchangers are:
- It has a more rugged design than other heat exchangers
- Comes in different sizes
- Since the device can be easily dismantled, cleaning and repair is relatively straightforward
- It can stand more process and physical abuse
- It can withstand very high temperatures and pressures
- The pressure drops and pressures can be varied over a wide range
- Since the device is made using different materials it has substantial flexibility. It can withstand corrosion and several other problems.
- Boiling heat transfer/condensation can be easily accommodated in either shell or the tube of the device, and the orientation is vertical or horizontal.
- You can enhance the heat transfer via the extended heat transfer fins
You have to make serious considerations when choosing cooling liquid options.
In the majority of cases, the cooling medium that is chosen is often one that is readily available.
When you look at most of the plants that use this device, you notice they have a constant supply of water.
Similarly, the plants have a good network that helps in pumping artificial coolant mix all through the plant.
Some of the most common cooling mediums/substances are:
- Propylene Glycol; applications that require a less toxic coolant often go for PG over EG. Otherwise, PG has similar properties as EG such as freezing point, boiling, and thermal transfer modification qualities.
- Water; it is the most effective in the majority of applications. It is often used to cool the premise. Water exhibits great and sufficient thermal qualities, low cost, and plain water.
- Ethylene Glycol; is a cooling fluid used in several places, especially where there are very extreme demands of a coolant. To create a coolant mixture, you have to mix Ethylene Glycol with water. The final substance has a higher boiling and lower freezing point. pEG is however toxic.
The choice of a Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger by several criteria as shown below:
- The level of maintenance (check the frequency of cleaning)
- Required ease of maintenance (pharmaceutical exchanger, FDA standards and others)
- The pressures involved (acceptable loss of head, design and maximum service pressure etc).
- The temperatures (temperature difference, temperature pinch, thermal exchange coefficient, temperature cross etc).
- Nature (fouling, clean, corrosive, viscous etc).
- The fluids involved (gas/gas, liquid/vapor, liquid/liquid etc).
Before you buy a Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger you have to ensure that it meets some of the quality standards.
And, this is shown by some certifications that allow it to satisfy a number of requirements.
The certifications must cover aspects such as the design, installation, and production of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers.
Some of the certifications include:
- HPO certification is for the German market
- SELO certificate for China market
- Stamp-U for Global market
- Certification of pressure vessels often compliant with module H/H1 for Europe market and PED 2014/68/UE
Below are some of the tests performed on Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers during design, manufacture and inspection:
Tube heat exchanger
- Radiography
- Penetrant examination test
- Hydraulic test
- Air/helium tightness test
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers have a warranty of more than 2 years.
It is however imperative to understand that the warranty of a device depends on the manufacturer/supplier.
At FilSon Filters, we design and manufacture a range of shell and tube heat exchangers to the specific requirements of your application needs.
Contact us today for custom and cost-competitive shell and tube heat exchanger systems.