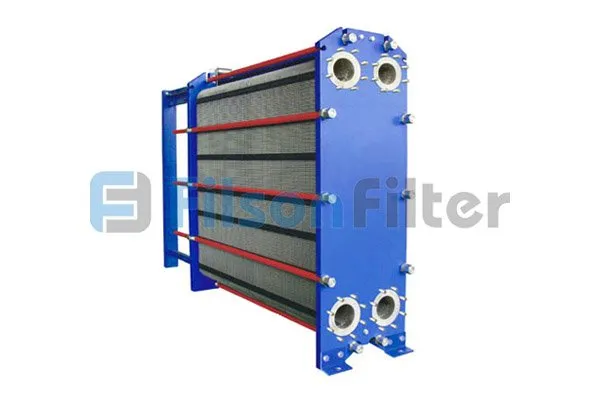
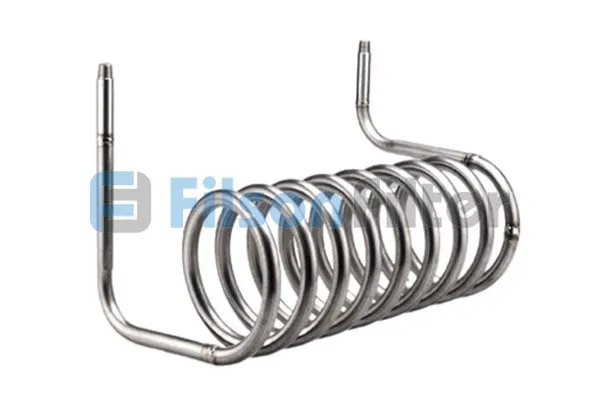
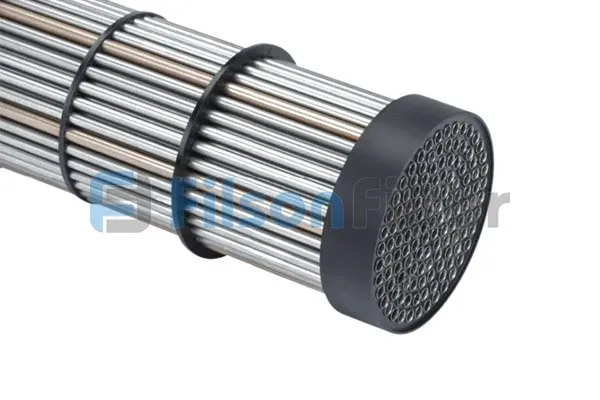
Filson Titanium Heat Exchanger
- High heat transfer efficiency
- Superior corrosion resistance
- Extended service life comparing to other heat exchanger
- Fully welded construction to eliminate the breakage during transportation and installation
- Durable and easy installation & maintenance
- Specifications
- Send Us Inquiry
Filson designs and manufactures heat exchanger in various materials. Among which the most frequently-used material is stainless steel. And the second commonly used material after stainless steel is titanium.
- Material: titanium
- Media type: oil, water, air, gas, stream
- Working temperature: -28.3-207.78℃
- Working pressure: maximum to 1.31Mpa
- Heat exchange area: 1 – 800㎡
- Color: grey, blue, silver, brown(based on customer requirements)
- Standard: ASME, ANSI, JIS, GB
Send Your Inquiry Today
Filson Titanium Heat Exchanger
Custom Titanium Heat Exchanger Based on Needs
Filson adopts different grades of titanium to construct heat exchanger. Pure titanium of grade 1 – 4 is the most popular material to build this product. This kind of heat exchanger possesses the properties of excellent corrosion resistance and good mechanical strength.
Combined careful structure design with excellent heat transfer performance, Filson titanium heat exchanger is made into various types such as plate heat exchanger, shell and tube heat exchanger, finnen tube heat exchanger, microchannel heat exchanger and so on.
Due to its highly anti-corrosive property, particularly due to its immunity to sea and salt water, Filson titanium heat exchanger is a preferred device for the marine industry. Another advantage of titanium material is its density, it provides weight savings up to and above 50%.
Filson is an expert in the field of heat transfer and Filson manufactures a number of titanium heat exchanger every year. With rich experience and professional expertise, Filson has the confidence to be your best and premier supplier for heat exchanger.
Titanium Heat Exchanger: The Ultimate FAQ Guide
This guide covers everything you need to know about the titanium heat exchanger system.
From parts, working principle, operating parameters to connection types, you will find everything about titanium heat exchangers here.
Keep reading to learn more.
- What is Titanium Heat Exchanger?
- Why use Titanium Material for Heat Exchangers?
- What is the Life Cycle Benefits of Titanium Heat Exchangers?
- What is the Maximum Pressure of Titanium Heat Exchangers?
- Which Designs of Titanium Heat Exchangers do you have?
- Which Titanium Heat Exchanger Properties should you look for?
- What are the Main Parts of Titanium Heat Exchangers?
- How does Titanium Heat Exchangers Work?
- What are the Titanium Heat Exchanger Applications?
- What are the Limitations of Titanium Heat Exchangers?
- How much does Titanium Heat Exchanger Cost?
- What is the Cooling/Heating Capacity of the Titanium Heat Exchanger?
- What is the Operating Temperature of Titanium Heat Exchanger?
- What are the Quality Tests and Inspections for Titanium Heat Exchanger?
- What are the Connection Types for Titanium Heat Exchangers?
- What Causes Failure in Titanium Heat Exchangers?
- When should you Replace Titanium Heat Exchangers?
- Is there Alternative Material for Titanium Heat Exchanger?
What is Titanium Heat Exchanger?

Titanium heat exchanger
A heat exchanger system facilitates the transfer of heat energy from one system to another.
You can use them for both heating and cooling processes.
Although you can make heat exchangers from different metals, these systems are made from titanium metal.
Unlike the other predecessors, titanium heat exchangers are totally immune to corrosion.
However, to work at full efficiency the device requires more surface area and a higher fluid flow rate.
In most cases, you will find coil patterns.
This is because they maximize the surface area of the tubes.
Why use Titanium Material for Heat Exchangers?
There are different grades of titanium used in the manufacture of this device.
Pure titanium of grade 1-4 is the most preferred material.
Grade 2 is also commonly used.
This is due to properties such as formability, excellent corrosion resistance, and moderate strength.
It has a high specific strength.
This feature reduces the weight and volume of the device.
It is, therefore, 45% lighter than steel.
It has good corrosion resistance.
You can even use aqua regia and it will not corrode the titanium walls.
In addition to this, you can design the walls to be thinner as this improves the heat transfer efficiency.
The titanium surface is easy to clean, smooth, and not easy to produce dirt.
Dropwise condensation is the condensation method on the surface of this device.
As such, there is a low wettability of liquid to titanium.
This condensation type greatly increases the heat coefficient and keeps the device updated.
Due to its durability, this device can eliminate any breakage during installation, handling, and operation.
It is used as part of welded-construction.
Titanium has an extended life service as compared to other materials of construction.
What is the Life Cycle Benefits of Titanium Heat Exchangers?
Titanium heat exchangers can function for decades if properly maintained.
This property makes the device economical to use.
They are also cost-effective over the whole life cycle of the device.
As compared to other materials of construction, the Titanium heat exchanger has an extended service life.
Some of the life cycle benefits of Titanium heat exchangers are:
- Ends breakage during operation, installation and handling because of fully-welded metal construction
- It accommodates high steam pressure to decrease needed surface area
- It gives high heat transfer efficiency
- It provides excellent corrosion resistance
- With this device, you need a spare parts inventory
- Do away with expensive downtime which occurs as a result of equipment failure
- Guarantees an extended service life as compared to other construction materials
What is the Maximum Pressure of Titanium Heat Exchangers?

Titanium heat exchanger system
The maximum pressure of the Titanium heat exchanger is 190 PSI.
There are those with maximum pressures of up to 90PSI.
The value depends on the intended application of the device.
This device can withstand very high pressures as they are used in applications requiring high-pressure environments.
Which Designs of Titanium Heat Exchangers do you have?
Titanium heat exchangers are built according to TEMA standards.
The designs vary depending on the mechanical demands of the applications.
They are also built in accordance with all of the main pressure vessel codes and international design standards.
These devices can weigh up to 200 tons, have diameters of up to 120’’ and 300’ in length.
When designing devices, you pay more attention to the dimensions, weight specifications, and performance.
Some of the designs of Titanium heat exchangers available include:
· Titanium Plate Heat Exchangers
This device is made using corrugated titanium plates.
It is suitable for liquid-steam and liquid-liquid heat exchangers.
The plate is very stiff so it can bear higher pressure.
The corrugation of the plates is to enhance the flow resistance and heat transfer efficiency of the device.
The plates can be horizontal flat or Z- shaped depending on the application.
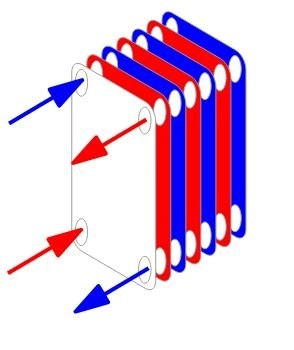
Plate heat exchanger
· Titanium Heat Exchanger Tubes
This heat exchanger has a titanium tube that effectively agitates the refrigerant and water.
It has an expanded surface area that maximizes the device’s contact with other main parts.
Due to this property, the device provides heat transfer at a higher rate.
Further, the tubes of this device are often uncoated remaining bare.
Heat exchanges tubes
· Titanium Frame Heat Exchangers
This device combines connections and frames to form a variety of configurations.
It is made using titanium material making it suitable for the chemical and marine industry.
· Titanium Marine Heat Exchangers
This device is used mainly in marine refrigeration. It is made solely using titanium material.
The tubes come in different shapes/designs.
· Titanium Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
This device is developed from high thermal performance tubes or reinforced traditional flat-tube shell tubes.
You can use a gas or liquid fluid in this device.
One type of fluid flows in the device’s tube and then out through the tubes in the shell.
· Pool Heat Pump Titanium Heat Exchangers
This heat exchanger is used specifically in swimming pools to warm the waters.
It is made using titanium material that can withstand corrosion or erosion of the device.
It is applied when a source of hydroponic heat is available.
You can use this device in a pool, Spa or even tub.
· Coil-type Titanium Heat Exchangers
It is often referred to as titanium cooling tubes.
Even after bending them, they do not easily deform.
Due to this property, the internal cooling liquid passes smoothly and produces superior cooling results.
· Row-Type Titanium Heat Exchangers
The tubes of this device are designed in such a way that they are row-shaped.
It is often used in an environment with less space.
Seeing titanium has high corrosion resistance, this device provides superior use performance.
Which Titanium Heat Exchanger Properties should you look for?
When selecting a suitable device for your application, there are some properties you have to give consideration.
The properties you should look for are:
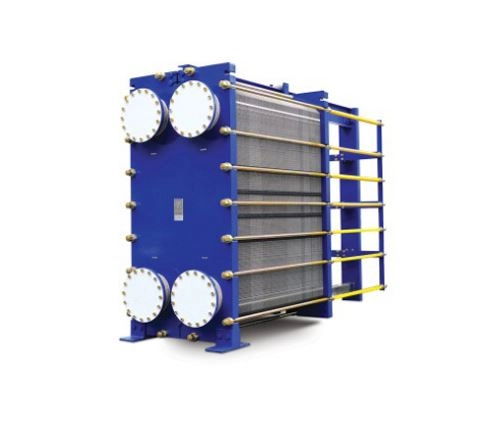

Titanium plate heat exchanger
· Rugged and Sturdy Construction
This device is made using titanium material that has excellent strength.
Titanium gives the heat exchanger this sturdy construction.
They can withstand any physical force applied to the casing of the device.
· High Heat Transfer Coefficient/Capacities/High efficiency
You can check the heating/cooling capacities of the device often included as part of the technical specifications.
The high-efficiency specification is also included so when a client selects the best device, they can access this information.
· Excellent Corrosion Resistance
When a heat exchanger is corrosion resistant, it can be used in different applications.
A fully corrosion-resistant device can be used in both salty or freshwater applications.
They do not have any erosion or corrosion of the surfaces of the tubes.
· Compact Design
With this design, the device is around 40% lighter or smaller.
It can fit in small spaces.
It also has different surface types that enhance the heat transfer coefficients and surface density of the device.
· Low-Pressure Drop
A device can have a low-pressure drop that triggers just enough turbulence to provide adequate and effective heat transfer.
Additionally, such an adequate pressure drop helps prevent any potential fouling in the device.
· Removable Tube Stacks making Cleaning an Easy Process
In titanium heat exchangers while cleaning, you can easily remove the tube stacks.
As such, you can clean and then return them back to their positions making it an easy process.
· Affordable Cost
Clients look for heat exchangers that are sold at affordable prices and are at the same time high quality.
Such a titanium heat exchanger can cost up to $1,000 or more/less depending on the supplier/manufacturer.
· Durable and Easy Installation
When buying such a device make sure to pick one that is easy to install.
It should also be able to withstand any pressure/temperature/physical force applied to it during transport, installation, and operation.
What are the Main Parts of Titanium Heat Exchangers?
A Titanium heat exchanger has several parts.
They all function towards completing an intended purpose – efficient heat transfer.
Some of the main parts of this device include:
· Titanium Tubes
The tubes are made using titanium material.
Tubes are small diameter pipes securely attached to the inside the shell.
It facilitates heat transfer creating the needed turbulence.
· Tube Sheets
Tube sheets isolate and support tubes in the titanium heat exchanger.
It is made from a flat piece of sheet with holes drilled to help the tubes stand in a pattern relative to one another.
Or, stand in the right location.
· Shells
A shell is the outer part of the device that encases the tube bundles.
On the surface of the shell are inlet and outlet pipes.
They bring in and out the fluids transferring heat in the device.
· Titanium Heat Transfer Plates
This component aids in heat transfer.
As fluids spread over the titanium places, it results in a large surface area for maximum heat transfer.
· Sealing Gasket
A gasket is a component that helps in sealing the device.
It joins the connections to the titanium heat exchangers.
· Pipe connection, flange and thread connection
These components act as the bridge between the device and the power source.
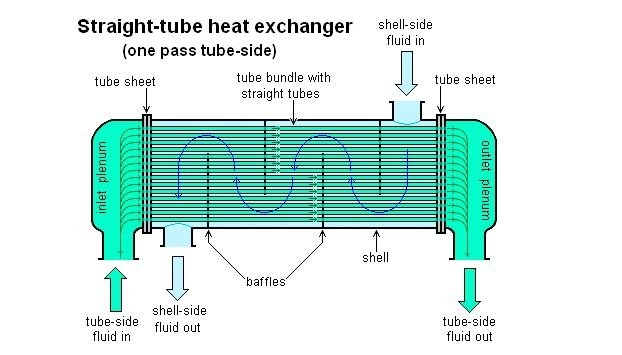
How does Titanium Heat Exchangers Work?
A Titanium heat exchanger helps transfer heat from one area to the other.
Put simply, inside a tube in the device, fluid flows via helical titanium encased in an insulated PVC barrel.
The second fluid flows over the titanium coil right inside the shell and rejects or absorbs heat depending on the intended purpose.
As the fluid flows in these tubes and pass one another, heat transfer takes place from the hot fluid to the cold fluid.
The fluid could take the form of a liquid/liquid, liquid/gas, or gas/gas.
The chosen fluid depends on the type of application for which it is intended.
In titanium heat exchangers without a helical coil, fluid flows through straight titanium tube bundles.
At the same time, water moves over and between these tubes.
Implying, there will be a larger surface area for cooling or heating.
The fluids involved (normally two) can flow at a right angle to one another.
That is, they can flow in opposite or same directions.
What are the Titanium Heat Exchanger Applications?
You can use a titanium heat exchanger in several applications because of its unique characteristics.
Further, this device is built in such a way that the titanium material used for its construction has a significant effect on its:
- Performance
- Quality
- Working condition
- Service lifespan
That said, you can use this device in the following applications:
- Marine engineering
- Oil and gas
- Swimming pools, spas, or hot tubs
- Freshwater aquaculture
- Waste water heat recovery
- Desalination
- Nuclear power industry shipbuilding industry
- Food industry
- Petrochemical industry
- Central heating
- Medicine
- Salt water heat exchange
- Sea food breeding
- Chemical industry
- Electronic communication
What are the Limitations of Titanium Heat Exchangers?
Titanium heat exchanger device is highly efficient for use in different applications.
It, however, has some limitations which impair its operation as well as choice such as:

Titanium heat exchanger system
· Cost
The initial cost of this type of heat exchanger is high.
You can spend around $1,000 or more on purchasing a new titanium heat exchanger.
The price also varies depending on the supplier/manufacturer.
One is likely to access an affordable device but still expensive in the least.
· Cracks/Leaks
Even though this device is made using titanium material which has high corrosion resistance, it can suffer serious leaks or cracks over time.
These holes in the device impact its ability to maintain turbulence or facilitate an efficient heat transfer all throughout the process.
· Fouling
This is a common problem in titanium heat exchangers.
Fouling reduces heat transfer across the surface of the device thus reducing the efficiency of this heat exchanger.
This type of heat exchanger is the most efficient as it has the least limitations.
The strengths of the device outweigh its weaknesses.
How much does Titanium Heat Exchanger Cost?
This device is cost-effective.
Only the initial cost is high, while the maintenance cost is low.
Since the device is high quality and durable you will not spend a lot on repair and maintenance.
It will take long before you have to conduct any maintenance on the device.
Overall, the operating and investment costs of the device are reduced.
What is the Cooling/Heating Capacity of the Titanium Heat Exchanger?
Since a titanium heat exchanger can be used for several applications, the cooling and heating capacities vary depending on the specific application.
The cooling capacity ranges from 1 -20 tons while the heating capacity ranges from 4 -375 tons.
What is the Operating Temperature of Titanium Heat Exchanger?
This is the temperature at which the device can function optimally.
It varies depending on the application context and function.
It has a minimum and maximum operating temperature range.
In this case, the operating temperature of the device is -19°F (minimum operating temperature) to 406°F (maximum operating temperature).
What are the Quality Tests and Inspections for Titanium Heat Exchanger?
According to TEMA and ASME Standards, you have to inspect the device before, during, and after manufacture.
Inspection is centered on the different components of the device such as the tube, plates, shell, and cooler among others.
Also, inspection is for assembly, dimension, and testing.
Below are some of the inspections and quality tests you can conduct on titanium heat exchangers.
· Pressure Testing
All Titanium heat exchanger samples must hold pressure proof of 800 PSI.
The devices are tested to burst pressure.
A burst at a specific temperature is shown by a leakage along the seam between the bar and header.
Often, this test is done in a swimming pool.
· Ultrasonic Testing
You can conduct this test to determine the integrity of the welded structure.
During the process, you will inspect various angles of the welded tubes.
Typically, there is a standard inspection of titanium heat exchangers as shown under the ASTM B338.
This test ensures that the device does not have any leaks.
· Eddy-Current Testing
This test is done to detect any cracks, pits, corrosion, and erosion.
You will conduct the test before putting this device into service to establish whether there were any damages during the installation and fabrication process.
It involves the use of electromagnet induction to detect and characterize any flaws on the surface of the device.
· Non-Destructive Testing
This test is done to evaluate the properties of the device; components, material, system or structure for welding defects or characteristic differences.
· Radiographic Testing
This test is done to determine the welding quality of the device.
An examination is done of the weld joints between the special connection fittings and device’s spiral manifolds.
An X-ray of the weld joints shows whether there are cracks or pores.
Once identified, the defects are re-welded to improve the quality of the joints/connections.
As such, the devices cannot leak when fluids are passed through them.
What are the Connection Types for Titanium Heat Exchangers?
This machine has two main types of connections:
- Flange; this connection makes replacement and removal easy.
- Thread; this connection makes assembly easy and simple as you only have to screw the parts together.
When used together, the two connection types improve the efficiency and operation of the heat exchanger.
What Causes Failure in Titanium Heat Exchangers?
Titanium heat exchangers often function at their optimum best.
However, they exhibit some failures which occur during operation.
Some of the causes of the failures in this device include:
· Clogged Air Filter
Clogged air filters cause the device to overheat resulting in stress cracks.
Stress cracks eventually cause leakages of the fluids in the tanks.
· Tube Corrosion
This problem occurs mainly in devices made with other materials other than titanium such as carbon steel.
Tube corrosion eventually leads to thermal permeation reduction resulting in the eventual deterioration of the tubes.
The tubes could be perforate and leak as fluid flow significantly reduces.
· Thermal Fatigue
The tubes of the device are often vulnerable to cracks and tears due to accumulated stresses associated with high-temperature differentials or constant thermal cycling.
If the device has a shell and tube side, it could suffer flexing.
This is because there is an extreme temperature difference between the two sides.
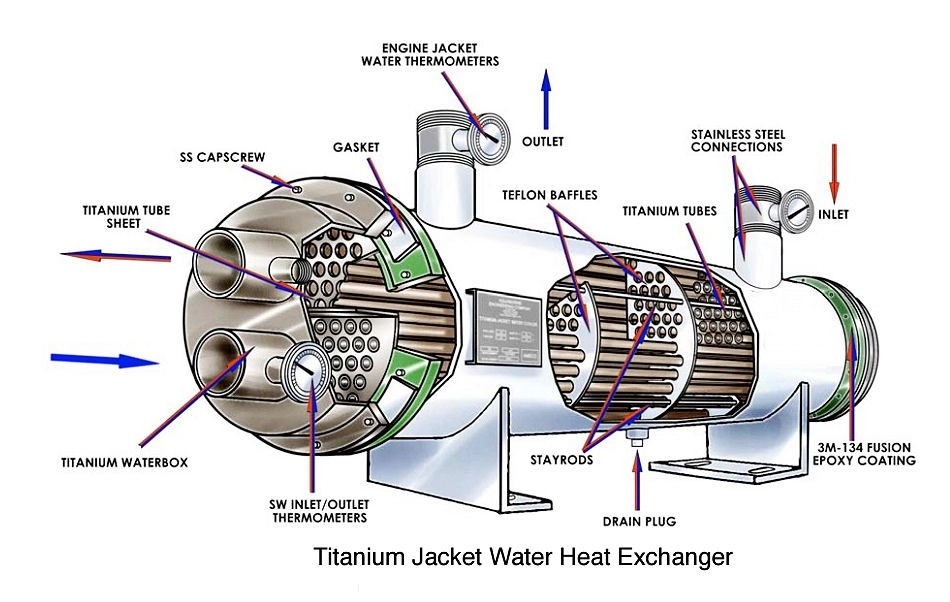
Titanium jacket heat exchanger
High-temperature differentials also occur due to the physical thermal expansion as well as contraction of tubes along their length.
These issues compromise the integrity of the connection of the tube and the tube sheet.
As a result, there is significant leaks in shell and tube heat exchanger systems.
· Vibration and Resonance
This problem results in the exertion of powerful forces on heat exchanger tubes.
Thus, increasing intensity up to a point where tubes fail and rupture.
It also increases intensity until the tube loses their seal with the tube-sheet and leak.
Excessive tube velocities can also result in this problem.
It results in abrasion between the tube and the baffle edge.
The tube’s bond with the tube-sheet could fail or the tube could rupture.
When should you Replace Titanium Heat Exchangers?
You can replace Titanium Heat Exchangers if the device experiences irreparable damage/failure.
At this point, the device has ceased to function.
Similarly, you can replace this device if it has wear and tears that hamper its efficient operation.
If the tubes are clogged, experience fouling or have serious cracks/leaks, you can replace them with new ones.
Is there Alternative Material for Titanium Heat Exchanger?
Yes, there is.
You can use different grades/types of steel such as carbon or stainless steel.
Also, you can use cupronickel, Monel alloy, brass, aluminum, and its alloys to make a Titanium heat exchanger.
Depending on your unique specifications, FilSon Filters offers a range of heat exchanger systems.
From shell and tube heat exchanger systems to gas heat exchanger systems, we offer high-performance heat exchanges.
Contact us today for all your titanium heat exchanger needs.


