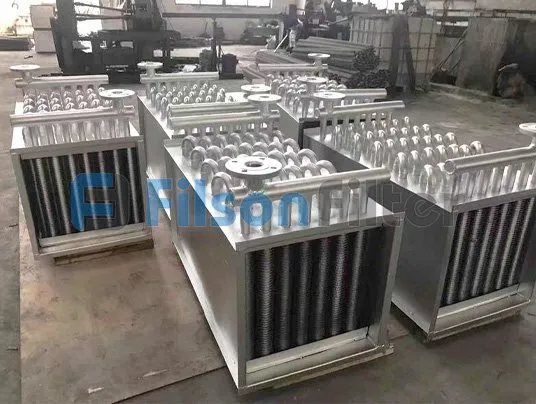
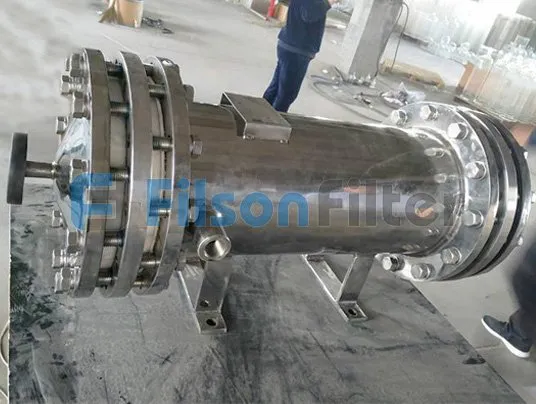
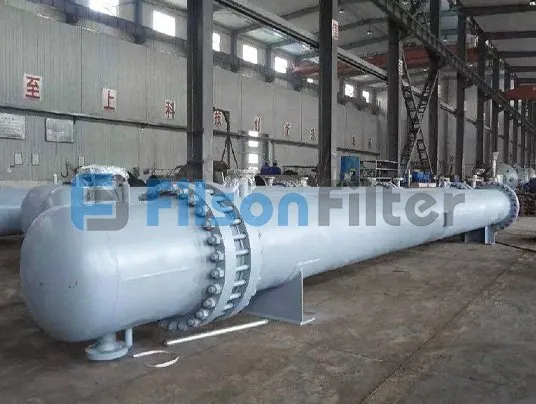
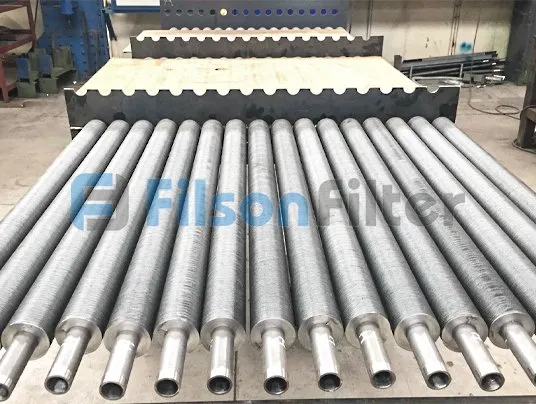
Your Reliable Tubular Heat Exchanger Supplier in China
As all other types of heat exchangers, Filson tubular heat exchanger is a heat exchange system or a heat transfer device between two kinds of fluids with different initial temperature. During the operation process, the two fluids exchange heat and reach a close temperature.
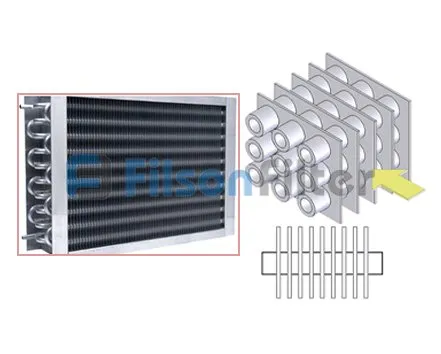
Filson tubular heat exchanger or tubular type heat exchanger, as its name implies, mainly takes tubes or tube bundles as the main body part. Undoubtedly, the heat transfer area is determined by the number and size of the tubes.
Tubular heat exchanger is a popular heat exchange equipment at Filson. Basically, it can be devided into several types: straight tube heat exchanger, U-tube heat exchanger, flat tube heat exchanger, titanium tubular heat exchanger, etc.
If you happen to be looking for a high efficient and cost-effective device for your application, don’t miss the following article. If you are here to order a tubular heat exchanger, contact Filson directly by filling the information sheet on the page.
Filson Tubular Heat Exchanger Supplier
Why Choose Filson Tubular Heat Exchanger
Firstly, Filson, as an expert in heat exchanger, has been exploring the design and manufacturing of tubular heat exchanger for more than 20 years. We know the product better than many other companies. And we are confident to be your most reliable supplier.
Secondly, Filson is a quality-oriented manufacturer. All tubular heat exchangers produced by Filson will undergo a series of rigious functional and safety tests. And before shipping, our specialists will conduct quality inspection to these products.
Thirdly, Filson provides a custom service. We not only manufacture standard type of tubular heat exchanger, but also develop custom type according to your requirements. And replacement tubular heat exchanger of other brands could be found at Filson.
Last but not the least, Filson has the best service through the whole process from quote to the final installation. We have a responsible team to solve any of your problems patiently. And for the delivery, Filson promises to satisfy your industrial needs as fast as possible.
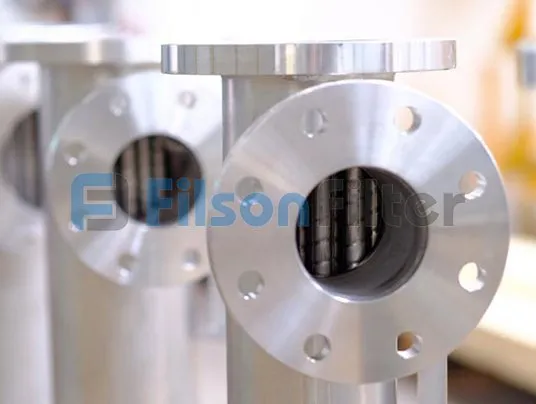

Filson: Professional Tubular Heat Exchanger for the Application
Filson tubular heat exchanger is an ideal equipment to be applied to a heating or cooling system to exchange heat between two fluids. When heat transfers inside the heat exchanger, the two fluids either absorb or release heat to realize its ultimate purpose.
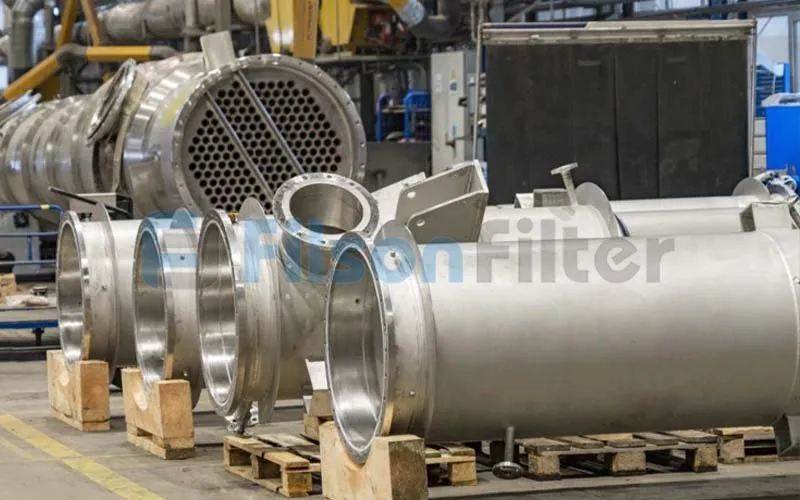

Filson tubular heat exchanger is a versatile type of heat exchanger with various configuration options. No matter for any size, structure, tube design, material or even color, Filson will provide a suitable tubular heat exchanger to fit your application.
If you ask the materials used to build a tubular heat exchanger, Filson will give you the most satisfactory answer. You are allowed to use a combination of different materials to make the device elements to meet your specific requirements.
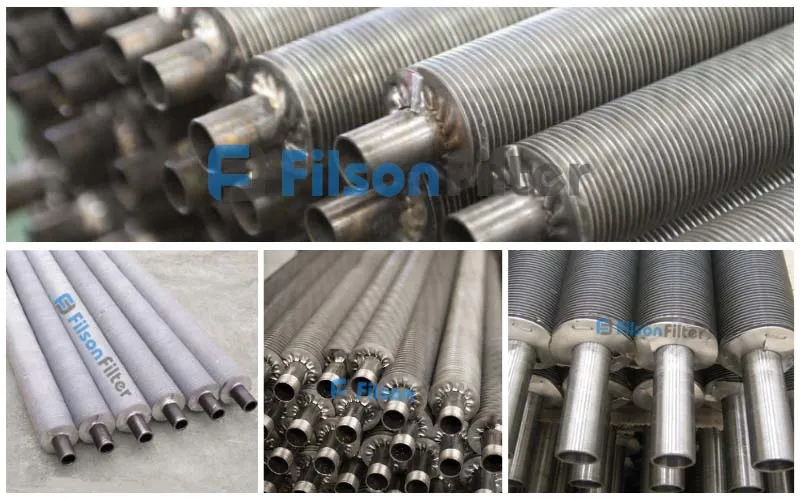

Beyond all question, stainless steel or titanium is always the optimal choice to manufacture a Filson tubular heat exchanger. In addition to these two materials, carbon steel, copper, aluminum, brass and alloys are also available for your custom tubular heat exchanger.
There are many different types of Filson tubular heat exchanger that have been mentioned above. Among which the most frequently-used type comes to shell and tube heat exchanger. With the unique ‘shell’ and ‘tube’ design, it’s really simple in structure and easy in operation.
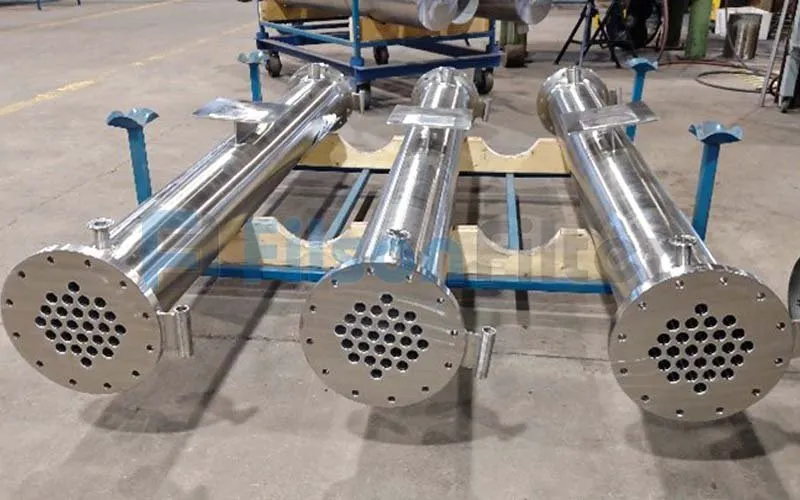

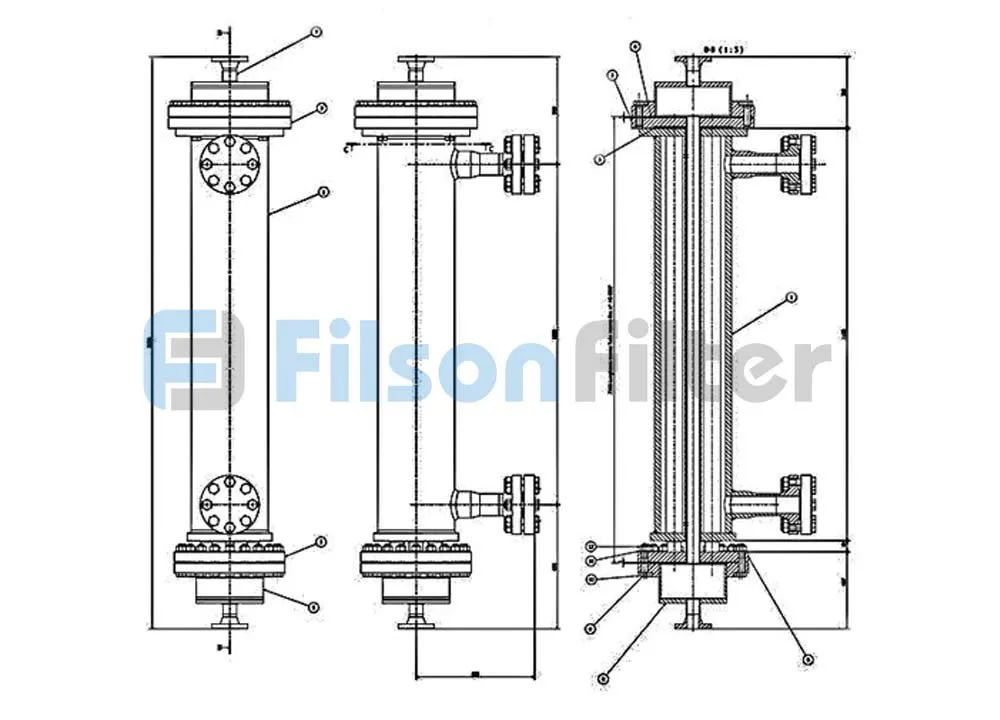
Filson shell and tube heat exchanger is mainly composed of shell, tube bundle, tube sheet and end head, etc. It is a typical dividing wall type of tubular heat exchanger which has a long history of industrial use and is still in the dominant position of all heat exchangers today.
Filson tubular heat exchanger has many different parts, just like a shell and tube heat exchanger. These elements will be manufactured respectively, and then the operators assemble them together to form the final device which is delivered to the customer.

As for the maintenance and debugging procedure of Filson tubular heat exchanger, we provide an on-site service if necessary. But in some special and particular times, we are prone to solve your problems by video which is both safer and cheaper.
By the way, Filson will prepare an instruction manual which is all in English along with your order. So that you can get a clear understanding of the tubular heat exchanger you purchased. Also, some matters needing attention are listed in the manual.

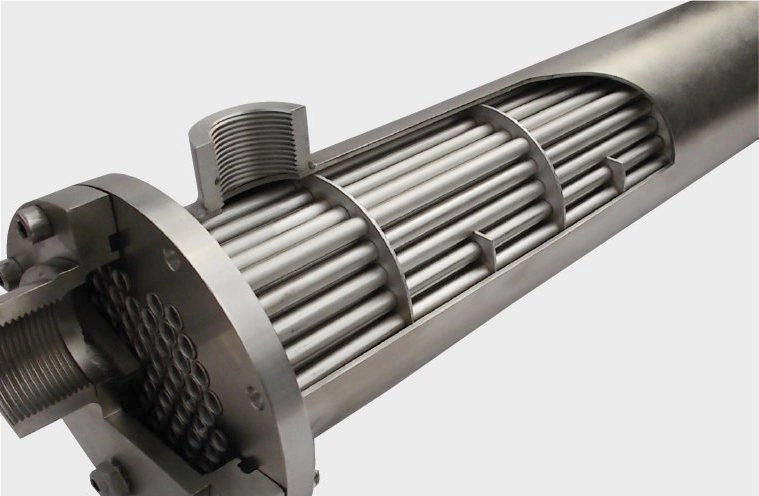
Generally, Filson has two tube designs for tubular heat exchanger: one is smooth tube, the other is corrugated tube. But the corrugated tube is more welcomed for its turbulence effect. A corrugated tube is a pipe with a helical shape through cold forming. It has higher efficiency than common smooth tube.
Filson tubular heat exchanger has a wide range of use. That means you can use various types of fluids in this device: viscous, particulate or clear. And the industrial applications that you can use a tubular heat exchanger in include thermal power, mine plant, petrochemical industry, urban central heating, food and medicine, machinery and light industry.
Filson has a strict series of processes after receiving your tubular heat exchanger order:
- First, our expert will analyze your application to make sure that the final manufactured device is available in the condition.
- Then, the properties of the fluids you are going to handle will be checked. The temperature, density, viscosity and thermal conductivity of the media are vital factors for a tubular heat exchanger.
- Next, Filson specialist will choose the correct configuration for your tubular heat exchanger.
- Further, the thermal calculations and mechanical design calculations will be conducted. Filson professional team is always responsible for your standard design specifications.
- Finally, a tubular heat exchanger drawing will be prepared for you to check after you decide all dimensions. Then it will be put into manufacturing.
Except for custom type tubular heat exchanger, Filson also has the ability to develop and produce replacement tubular heat exchanger of other leading brands to replace your old one. Each replacement has the same or even exceeding performance comparing to the original equipment.
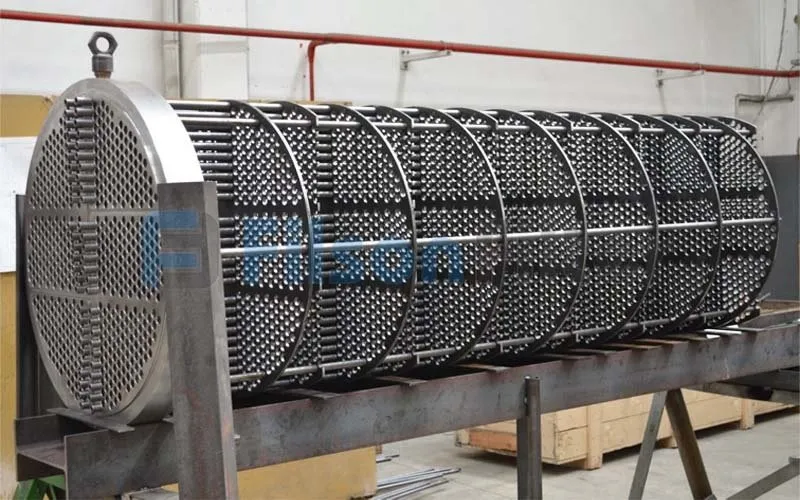

Filson is your reliable supplier and manufacturer for all tubular heat exchangers and replacements with better quality and lower price. If you want to know more advantages and disadvantages about tubular type heat exchanger, please contact us and get a quote now!
Contact Us:
Email: sales@filsonfilters.com
Whatsapp: +86-157 3695 8886
Address: Beihuan Logistics Park, Muye District, Xinxiang, Henan, China.
We are always looking forward to becoming your business partner in the future.
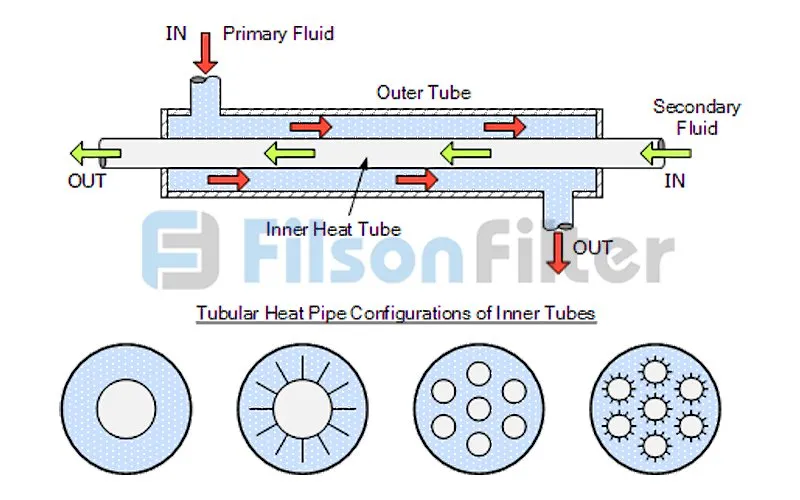
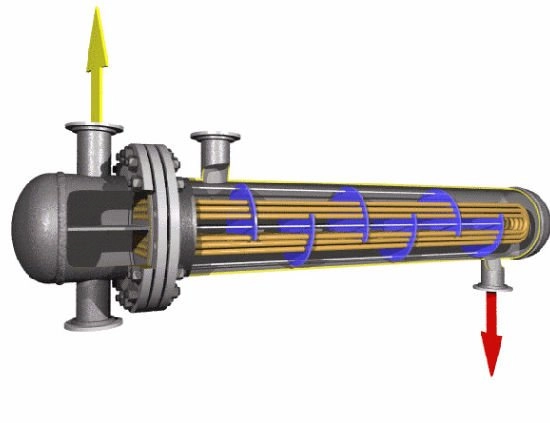
Tubular Heat Exchanger Working Principle:
Typically, there are tubes, baffles and tube sheets inside a tubular heat exchanger. The tubes are usually fixed to the tube sheets and the baffles are perpendicular to the tube bundle and have a circular notched shape. At the meantime, the tubes are welded into the round hole of the tube sheets.
When tubular heat exchanger works, one fluid passes through the tubes, while the other fluid flows through the gap between the baffles and the tube bundle. In this process, the baffles mainly serve to strengthen the heat transfer and support the tube bundle.
During the heat exchange process, the two fluids are separated by the tube wall which prevents the fluids from mixing. The hot fluid first transfers heat to the wall, and then the heat will be transferred to the cold fluid. That’s called a whole heat exchange process.
Filson tubular heat exchanger can realize either parallel flow or countercurrent flow inside the equipment. It’s mainly determined by the fluids inlet and outlet arrangement.
Filson Tubular Heat Exchanger Function:
- Improve heat transfer efficiency
- Reduce thermal resistance
- Recover waste heat
- Save energy and maxmize the profits
- Apply to heating or cooling systems
- Optimize heat transfer of every per unit volume
- Cut both disassembly and maintenance time
- Ensure safety of manufacturing process
Filson Tubular Heat Exchanger Feature:
- Obvious energy efficiency
- Flexible design to fit various specifications
- Wide application conditions
- High heat exchange rate
- Fluid streams(one or both) of high pressure
- Compact structure and small footprint
- Light weight and simple installation
- Long life service
Filson Tubular Heat Exchanger Specification:
- Material: stainless steel, carbon steel, copper, titanium, aluminum, composite material, brass, alloys
- Media type: oil, water, air, gas
- Structure: single tube, double tube, multi-tube
- Tube design: smooth or corrugated
- Working temperature: up to 400℃
- Working pressure: up to 6MPa
- Heat transfer efficiency: up to almost 100%
- Color: grey, blue, silver, brown(based on customer requirements)
- Standard: ASME, ANSI, JIS, GB
Filson Tubular Heat Exchanger Application:
- Food and beverage
- Chemical plant
- Paper industry
- Petrochemical industry
- Steel processing
- Electronic energy
- Pharmaceutical engineering
- Metallurgical industry
- Mechanical engineering
Tubular Heat Exchanger: The Ultimate FAQ Guide
Tubular heat exchanger is a heat exchanger system between a cold and hot fluid.
It provides practical solutions for your cooling and heating of products that could cause problems in alternate heat exchange methods.
You can use it in applications requiring a larger surface area.
Tubular heat exchanger
The decision to buy a tube heat exchanger is often very complex.
However, users can use the below features to make their choice.
- Easy installation
- Easy to clean as you can easily dismantle the tubes
- Low maintenance
- Cost
- Heat transfer efficiency
- Compact/robust design
- Both smooth and corrugated inner tubes
- Fully welded construction/sturdy construction
- Stainless/carbon steel construction guarantees a long service life
- Maximum allowable pressure/temperature
- High corrosion resistance
This device is often ideal for products with particulates or high viscous products.
They can maintain product integrity by gentle product handling.
However, still meet the requirements of your application.
Below are some of the places where you can apply your device:
- Biogas reheating and steam production
- Production of fuels
- Paper industry
- Steel industry
- Agriculture industry
- Energy industry
- Chemical industry
- Petrochemical industry
- Food and beverage industry
Below is the process of designing a tubular heat exchanger:
Tube heat exchanger
1. Analyzing the Application
These could be industrial applications, food industry applications, or any other applications.
The design engineer has to accurately define the type of heat exchanger needed and whether it would meet the requirements of the applications.
Some of the important data that you need to design a tubular heat exchanger are:
- Physical properties of the products
- Temperature
- Process flow rate
That said, the main process data to design a tubular heat exchanger are:
- Service and product flows
- Flows
- Outlet and inlet temperature
Such parameters verify the principle of energy conservation.
Flow rate, the maximum admissible pressure drops, and the pressure drop are equally important but they depend on the application.
2. Identify the Fluid Properties
Analyze the gases or fluids involved. The four main physical properties of the involved fluids are:
i. Specific heat
ii. Density
iii. Viscosity
iv. Thermal conductivity
3. Definition of Geometry of the Tubular Heat Exchanger
This step is about defining the geometry of the device.
You have to choose the right configuration for your tubular heat exchanger.
Such configurations consist of tubes, tube bundles, removable/non-removable tubes.
4. Thermal Calculation
Next, conduct the thermal calculation of the device to achieve the desired temperatures.
Since this device often uses a corrugated technology, there is a reduction in the length of the device as well as the number of interconnected units.
This technology also makes the device more compact, improves the coefficient of heat transfer and the turbulence.
5. Mechanical Design Calculations
Following this, you perform the mechanical design of the device.
A designer checks that the selected thicknesses for every element are in accordance with the required design code.
These elements include shell tubes, inner tubes, connections or tube bundle.
The design codes include PD5500, EN 13445, ASME Section VIII Div. 1 or AD2000-MERKBLÄTT among others.
6. Prepare the Manufacturing Drawings
You can prepare the manufacturing drawings once you have all the dimensions of the device defined.
A user can access a drawing package with details of all the components of the device.
To make this device, you can use stainless and carbon steel materials.
However, you can use a combination of different materials to make the device elements.
Some of these materials include Aluminum, copper, composite material, brass and alloys.
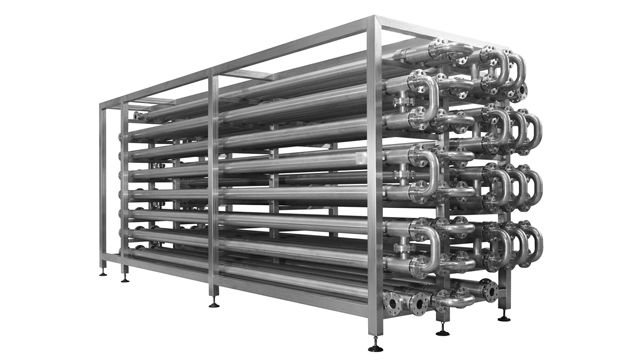
Tubular heat exchanger
Absolutely, yes.
Usually, tubular heat exchangers are assembled in the manufacturing plants where they are built.
Once the different parts of the device have been manufactured, the operators assemble them to form the final device which is delivered to the client.
Laboratory tests helps determine the main properties of a device.
Also, these tests aid in the characterization of the behavior of the product in an accurate way.
- Non-destructive test; just as the name suggests, it is a quality test used to determine the quality of the components, material or system without causing any damages.
- Pressure test; according to the ASME Pressure Vessel Code, ensure that the metal temperature during the test is 170C over the minimum design metal temperature. However, you should not exceed 480C to lessen the risk of brittle fracture.
This test is done on the tube bundle, shell and cover of the device for a period of around 15 minutes.
- Remote field testing; you can only use this test on THE if it is made using raw materials consisting of iron particles.
It examines the tubes of the device for thinning.
- Whole unit inspection/test; this test is about examining all the components of the device to ensure that they are in good shape and ready for use.
- Radiographic test; it saves not only on money but also time.
This test involves taking an X-ray of the welded parts of the device to identify areas that are weak, have fractures, porous or cracks.
This test is very important as it shows that the device is safe for use for longer periods.
- Hydrostatic test; this test helps evaluate the structural integrity of the device.
- Helium/Air tightness test; this test helps establish the energy efficiency of a THE as it identifies poor build quality within the device.
It involves introducing the device to a vacuum chamber and testing it using helium gas.
You seal the device in a chamber, close the lid of the chamber and pull the pump of the vacuum chamber.
The parts of the chamber are filled with helium.
This gas migrates to the part of the device which has leaks.
Helium test is often accurate, highly sensitive, cost efficient and the test method is independent of moisture and temperature.
- Penetrant Examination test; it identifies any discontinuities on the surface of the device. They could be overload fractures, fatigue cracks or grinding cracks.
- Eddy current testing; this quality test helps identify flaws in the tube.
Some of the flaws include de-alloying, cracks, subsurface voids or wall thinning.
- Inspection of the flanges, and inner surfaces of the tubes. After construction, the quality team thoroughly inspects these components to determine if they are safe for use.
- Expansion joint inspection; this test involves inspection of the connections and internal surface for erosion or corrosion.
It also involves an air test.
All these tests show whether the expansion joints have excellent structural integrity and are high quality.
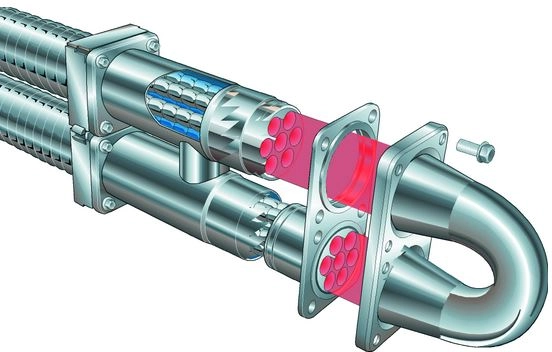
The basic components of a tubular heat exchanger are:
Tubular heat exchanges
- Tube bundle
- Tube sheets
- Baffles
- Shell
- Tubes
Others include:
- Ports
- Nozzles
- Tie rods
- Gasket
Of course, yes.
Tubular heat exchangers often have self-cleaning depending on the dust quantities and characteristics.
The cleaning device works by cleaning the surface of the device elements and removing excessive dust hence maintaining the efficiency of the tubular heat exchanger.
However, you can still manually clean the device by removing the different parts such as tubes, bundles and baffles then clean.
After cleaning, you return the components to their right places.
Cleaning the device improves its service life as its operation efficiency as it eliminates any potential failures.
Tubular heat exchangers work on the principle of forced draught convection.
The process gases move over the outside surface of the device’s elements.
There is generation of cooling air from ambient air centrifugal or axial fans and then blow along the pores of the device elements hence facilitating heat transfer.
There are design parameters and parameters of parts of the device.
The design parameters include:
Temperature is often 100C higher than the maximum operating temperature.
Pressure is usually 5-10% higher than the maximum operating pressure.
It is the same pressure value used to calculate the thickness of the shell.
Parts parameters:
Shell; the internal diameter of the shell relies on the outer tube limit.
This part can be made using a standard pipe.
The tubes of this device are often plain.
The tube length includes length of tubes inside tube sheet, distance between two tube sheets and any extension outside tube sheet.
The total number of tubes relies on the outer diameter of the tube and heat transfer area.
Tube sheet; you can always use a tube sheet with a flange if the tube sheet material is affordable (carbon steel).
However, you can select a tube sheet without flange if the material is expensive (stainless steel).
Gasket width; this feature’s thickness is based on the sizes established by the manufacturers.
Tube configurations; the configurations come in four options.
There are triangular, square, rotated triangular or rotated square pitches.
Triangular and square pitch are the common configurations and this is because they facilitate easy cleaning of the external parts.
The tubes are often not arranged symmetrically in tube sheet.
There is extra entry space in shell through eliminating tubes directly under inlet and outlet nozzle.
Nozzles; there are inlet and outlet nozzles, drain outlets and connections.
Baffles; chose the best baffle for your device.
Material of construction; the type of material chosen for the entire device or components vary depending on the intended application, fluid or general properties of the material.
Tie rods; the diameter of this component depends on strength needed.
The length of the tube predicts the length of the tie rods.
You can use 4-6 tie rods.
When designing the device, you have to determine the thermal exchange coefficients accurately and reliably.
However, to calculate a tubular heat exchanger, you must knowledge of the thermal properties.
These properties include specific heat, density, viscosity and conductivity.
A designer must know the variation of these above properties at different temperatures within the working range.
Next, you perform a thermal design of the tubular heat exchanger.
A designer has to first calculate the optimal exchange area that easily fulfills all the requirements suggested by the client.
You then apply the next heat transfer equation of .
In this case, Q = thermal exchange duty, U = global thermal exchange coefficient, A = exchange area and LMTD = logarithmic mean temperature difference.
This equation is applied to several number of sections of the device.
Further, the heat transfer efficiency of the device between the fluids differ along the equipment.
Thermal properties change with temperature as well as complex thermal phenomena taking place in the device.
To determine the thermal duty of the device, use this formula,
It relies on the process data already available from the product, and will always be processed from the inner tube.
Use the below formula to calculate the Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference
This feature depends on the outlet and inlet temperatures of the device and service fluids.
Next, to determine the overall heat transfer coefficient, add different thermal resistances using the below formula
Finally, calculate the required exchange area
You can obtain the heat exchange area by applying the heat exchange equation.
Since you have the diameter of the inner tube area, you only have to include the total length of the device using the below formula
The answer from this equation is in theory the required area of the device.
If the length of the device is less than the theoretical one then a whole set of heat exchangers (n) is needed to be placed in the series.
Use this formula to achieve this goal
Typically, it is preferable for the heat exchange area to be higher than the theoretical one.
There is uncertainty when evaluating the thermal properties of the fluids, the heat transfer coefficients or the fouling resistances.
You can use the below formula to quantify the fouled K-value, general thermal exchange coefficient or the overdesign.
Tube heat exchanger
Usually, tubular heat exchangers can have either smooth or corrugated inner tubes.
However, the best choice is a corrugated inner tube.
A corrugated inner tube is a pipe with a helical shape collected from a plain tube through cold forming.
Corrugated inner tubes optimize performance and heat transfer.
Further, original mechanical properties of the smooth inner tubes remain making the corrugated tubes more efficient than the latter.
Overall, tubular heat exchangers are cost-effective.
There are some tubular heat exchangers that cost less than $500, and those that cost up to $20,000.
The price depends on factors that such as the size, intended use, materials and availability of spare parts.
The cost of a tubular heat exchanger includes the raw materials, design, manufacture, installation, maintenance and shipping costs.
If you use carbon steel material to build your tubular heat exchanger you will accrue less costs because it is less expensive.
However, if your stainless-steel material which is often expensive, you can accrue higher costs.
If the design of your device is complex, you will require special machines or experts on build the THE hence attracting higher costs.
Since the device is high quality and durable, it has a longer service life which could run up to 20 years.
You do not need to constantly conduct maintenance services on the device hence lowering the maintenance costs.
You can use various types of fluids in this device; viscous, particulate or clear:
- Air
- Gas
- Glycol; ethylene and glycol
- Water
- Deionized water
- Hydraulic/motor/machine oil
You can guarantee the quality of your tubular heat exchangers by creating a powerful quality control team who controls the quality in each production process.
In addition, the devices have the quality standard marks such as CE/ASME/TEMA that show that quality inspection and tests have been done on the tubular heat exchangers.
They are, therefore, high quality and safe for use by customers.
Typically, the service life of a tubular heat exchanger falls between 10 and 20 years depending on several different factors.
You can choose to replace the entire device or the faulty components.
If your device has minor cracks you can repair them to prevent further safety threats and damage.
However, if the cracks are large and serious, you can replace the entire device.
Replacement can also occur if there are airflow issues within the device.
Usually, airflow issues may contribute to the overheating of the device thus fully impairing its operation.
If you detect any of these failures/risks, you have to have to replace your device with a new one.
Tubular heat exchangers often have a warranty of more than 1 year.
There is warranty for the tubular heat exchanger and another one for the core components.
The warranty begins from the day of the delivery to when the time frame ends.
It covers any manufacture defects but not physical damages inflicted on the device by users.
The working temperature of a tubular heat exchanger varies depending on the intended application.
It can range from – 50 – 150℃
Some of the disadvantages of a tubular heat exchanger include:

Tube heat exchanger
- Fouling is a serious problem in this device, especially for those with small sized tubes.
You, therefore, have to clean your device frequently to avoid fouling and this is tiring.
- The initial cost of a tubular heat exchanger is high. A single device can cost as high $20,000.
Even though the maintenance costs are low, one must have a large sum to be eligible to purchase the device itself.
- Preventing leakages or repairs in this device is difficult.
Unless you perform these various quality and inspection tests can you identify the areas with flaws.
- There is highly likely to a pressure drop in the device. As such, you have to keep checking the components of the device.
- Cracks are common in tubular heat exchangers due to the use of steel materials as well as exposure to hot/cold fluids at high pressures
With the different forms of heat exchangers available in the market, tubular heat exchanger is the most popular form in use.
The main reasons for this choice are:

Tibular heat exchanger
- High working temperature of up to 285°C
- High working pressure up to 871 psig/60 bar
- Low maintenance cost
- Easy disassembly and inspection. The tubes are easily dismantled for cleaning.
- Easy to enlarge
- Some have a self-clean device
- Efficient heat transfer
- High security in aseptic processes
- Processing of fibre or particulate matter
- High flexible in raw materials of construction from special alloys to carbon steel
- Are versatile
- Are sold at competitive prices
- Have a compact/robust design
- Sturdy construction
- Resistance to fouling
As you can see, the tubular heat exchanger system plays an integral role in modern industrial setups.
However, its efficiency and reliability depends on your ability to choose the best tubular heat exchanger.
At FilSon Filters, we have a range of heat exchangers systems such as tube and shell heat exchanger, gas heat exchanger, titanium heat exchanger, and gas cooler heat exchanger, amongst others.
In case you have any question or inquiry, talk to the FilSon Filters team now.